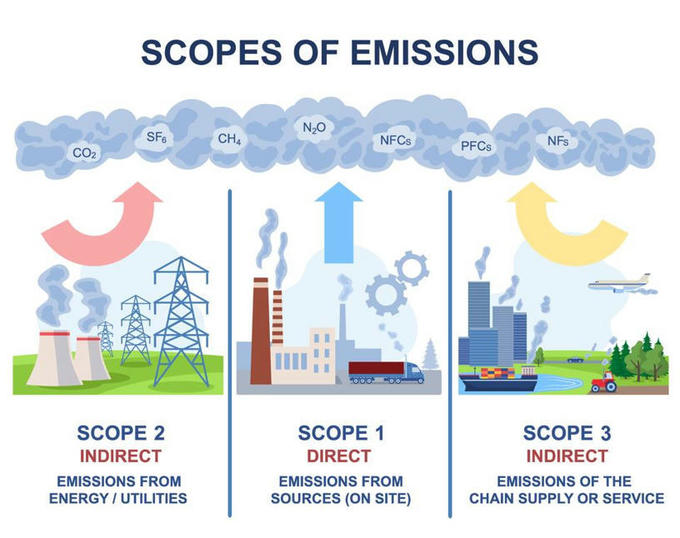
The global landscape is moving towards more transparent climate disclosures. Businesses are expanding their reporting to cover emissions from direct operations and their entire value chain, including suppliers. For reporting purposes, emissions are classified into three types: Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3. Reporting Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions (direct emissions and indirect emissions from purchased electricity) is straightforward, but Scope 3—indirect emissions from the entire value chain—is more complex. Scope 3's reporting challenge stems from data scarcity, poor data quality, and numerous calculation assumptions. However, reporting on these emissions are essential as they constitute over 70% of a company's total emissions. Therefore, despite its novelty and complexity, navigating this landscape has become crucial to address climate change.

About the Author

EcoVadis is a purpose-driven company dedicated to embedding sustainability intelligence into every business decision worldwide. With global, trusted and actionable ratings, businesses of all sizes rely on EcoVadis’ detailed insights to comply with ESG regulations, reduce GHG emissions, and improve the sustainability performance of their business and value chain across 220 industries in 180 countries. Leaders like Johnson & Johnson, L’Oréal, Unilever, Bridgestone, BASF and JPMorgan are among 150,000+ businesses that use EcoVadis ratings, risk, and carbon management tools and e-learning platform to accelerate their journey toward resilience, sustainable growth and positive impact worldwide.
Follow on Linkedin
Visit Website
More Content by EcoVadis EN
Follow on Twitter Follow on Linkedin Visit Website More Content by EcoVadis EN


